OVERVIEW - CORPORATE TRAINING
The high pressure work environment which is focused on the achievement of targets in a very tight time schedule leaves a young corporate executive groping for solutions. Individual achievements are things of the past. In today’s technology driven world, team work is the bedrock of all success. People who learn to work in teams never fail. In today’s environment, it has become imperative to have high performance teams.
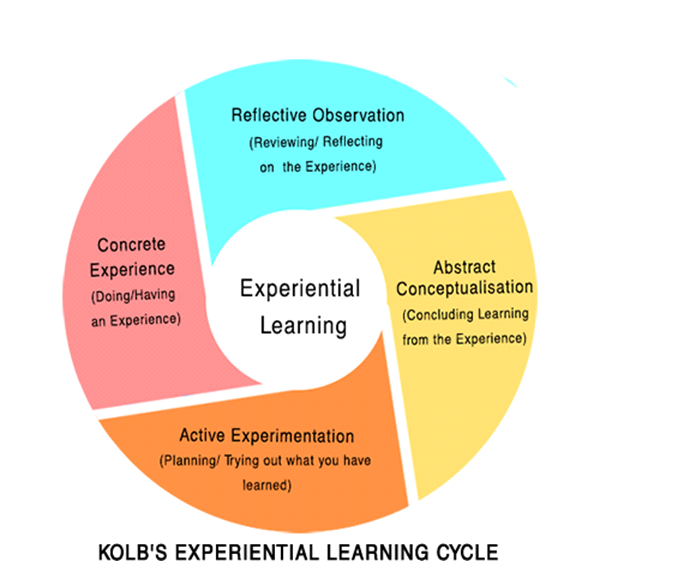
Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is a method that moves away from the theoretical and parrot-fashion learning methods of traditionalist education. Some things simply cannot be learned from books or lecture, so experiential learning is a natural and constant life process on which all development training, particularly Management Development Outdoors aims to capitalize. Experiential learning can be seen as a four-stage cycle -
- Concrete, personal experiences followed by :
- Observation of and reflection upon one's experiences, which leads to :
- The formation of generalizations and abstract concepts, leading to :
- Hypothesis to be tested by future actions, which in turn lead to new experiences
Benefits - Discover through Team Outings
Outbound team building activities, team outing and experiential learning has been shown to -
- Improve communication, problem solving and team work.
- Build self-esteem and self-confidence.
- Improve group dynamics and learning to function as a cohesive unit.
- Help teams identify their strengths and areas for improvement
- Develop self-awareness, leadership and social skills
- Appreciate the benefit of physical activities and a healthy life style.
- Build trust among participants and grow together in an unfamiliar environment
Key Concepts of Building Teams
With the help of experiential learning, we can develop various competencies and achieve our objectives. Key concepts of leadership /group dynamics and building effective teams are explained below-
Team Development
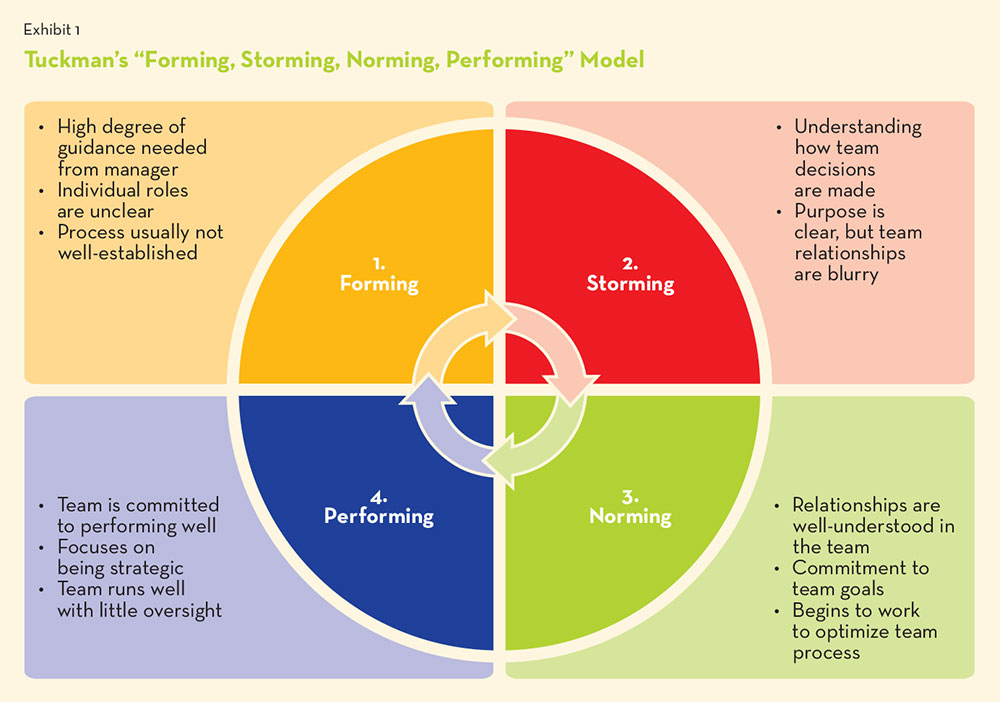
All organisations follow the concept of working in teams whereas size of teams could vary depending on the task or project. It could be creating small teams out of a big team for a specific project or create sub – teams, may be under same project. Irrespective of size or type, all teams go through a number of phases or stages which is explained by the Dr Bruce Tuckman’s model, which has four stages - Forming, Storming, Norming, and Performing.
Dysfunctions of a Team
Not strategy or technology, but it is teamwork that remains the ultimate competitive advantage. Genuine team work in most organisations remains elusive and fails to achieve results. Creation of new or project teams is the simplest job whereas managing the stages of development of teams has become a tedious task. During these stages, teams face numerous challenges which are termed as Dysfunctions as described by Patrick Lencioni. These dysfunctions are explained as under –
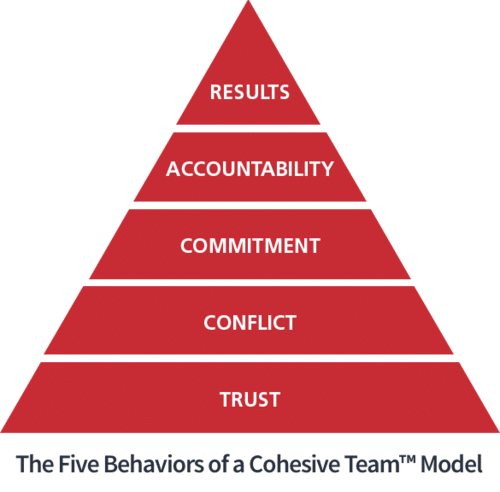
- Absence of Trust - T•The first dysfunction is an absence of trust among team members. Team members who are not open with one another about their mistakes and weaknesses make it impossible to build a foundation of trust.
- Fear of Conflict – •Failure to build trust leads to the second dysfunction i.e. Fear of conflict. Teams that lack trust are incapable of engaging in unfiltered and passionate debate of ideas.
- Lack of Commitment – •Lack of healthy conflict is a problem because it ensures the third dysfunction of a team Lack of commitment. Without having healthy and open debates, team members rarely, if ever, buy - in and commit to decisions.
- Avoidance of Accountability – Due to lack of real commitment and buy –in, team members develop an avoidance of accountability, the fourth dysfunction. Without committing to a clear plan, even the most focused and driven often hesitate to call their peers on actions and behaviours that seem counterproductive.
- Inattention to Results – •Failure to hold one another accountable creates an environment where the fifth dysfunction can thrive. Inattention to results occurs when team members put their individual needs above the collective goals of the teams.
"Every young person should experience the world beyond the classroom and office as an essential part of learning and development whatever their age, ability and circumstances"


